About This Template
Feeling lost in the world of stroke information? Our FREE Stroke Concept Map Template offers a clear visual framework to organize knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of this condition.
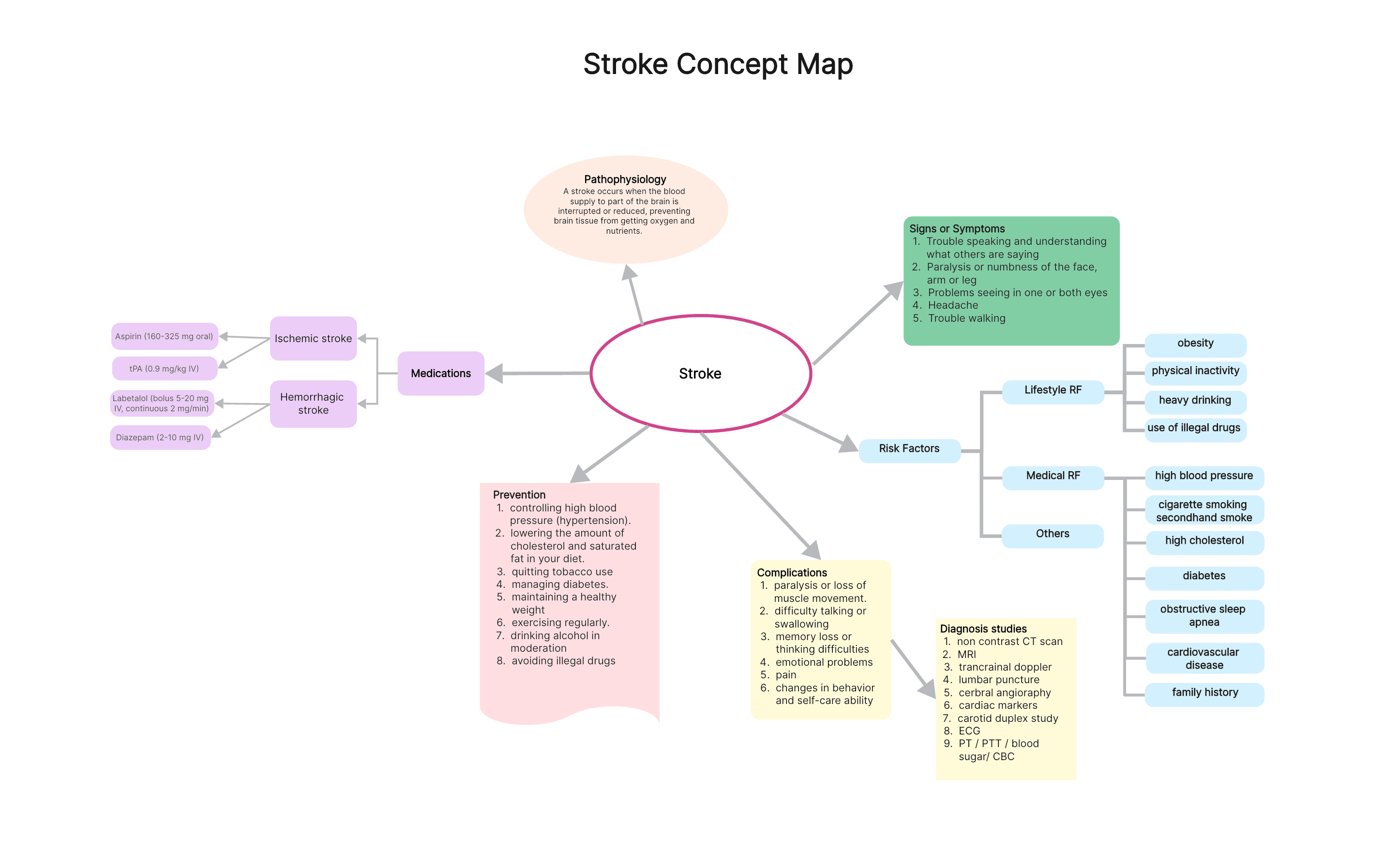
What is Stroke?
A stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die in minutes, leading to sudden loss of function. Strokes are a leading cause of disability and death worldwide. There are two main categories of stroke, each with distinct causes and effects:
- Ischemic Stroke: This is the most common type of stroke, accounting for about 85% of all cases. It occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, preventing blood from reaching brain tissue. Blood clots can form due to various reasons, including:
- Atherosclerosis: This is the hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup.
- Heart arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can dislodge blood clots from the heart that can then travel to the brain.
- High blood pressure: Chronically high blood pressure can damage blood vessel walls, making them more prone to clotting.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a weakened blood vessel in the brain bursts, bleeding into the surrounding tissue. This bleeding disrupts normal brain function and can cause significant damage. Causes of hemorrhagic stroke include:
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure is a major risk factor for hemorrhagic stroke.
- Aneurysms: These are weak spots in blood vessel walls that can bulge and eventually burst.
- Blood thinners: Medications used to prevent blood clotting can increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke if not carefully monitored.
The specific effects of a stroke depend on the location and size of the affected brain area. Different brain regions control various functions, so stroke symptoms can vary widely.
Symptoms of Stroke
The acronym FAST can help you remember the most common stroke symptoms. Act quickly if you experience any of these signs:
- F: Face drooping - Does one side of the face droop or feel numb? Ask the person to smile. Does one side of the face appear uneven?
- A: Arm weakness - Can the person raise both arms equally? Ask them to hold their arms out straight with palms facing down. Does one arm drift downward?
- S: Speech difficulty - Is speech slurred or difficult to understand? Ask the person to say a simple sentence. Is their speech garbled or nonsensical?
- T: Time to call emergency services - If you experience any of these symptoms, call emergency services immediately. Time is critical in stroke treatment. Early intervention can minimize brain damage and improve recovery outcomes.
Additional Stroke Symptoms
- Sudden numbness or weakness in one side of the body: This can affect the face, arm, or leg, or one entire side of the body.
- Vision problems: Sudden blurred vision, complete vision loss in one eye, or double vision can occur.
- Severe headache: A sudden, severe headache without a known cause may be a sign of stroke.
- Difficulty walking: You may experience dizziness, loss of coordination, or difficulty maintaining balance.
- Confusion: Sudden confusion, difficulty understanding speech, or problems with thinking and reasoning can occur.
Causes of Stroke
Several factors can contribute to an increased risk of stroke. Understanding these risk factors allows you to take proactive steps to prevent stroke:
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure is a major risk factor for both ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
- High cholesterol: High levels of LDL ("bad") cholesterol can contribute to atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Diabetes: Diabetes damages blood vessels and increases the risk of both stroke and heart disease.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases your risk of stroke-related risk factors like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle increases your risk of stroke.
- Family history of stroke: Having a close relative with a history of stroke increases your risk.
- Age: The risk of stroke increases with age.
- Certain medical conditions: Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat), sleep apnea, and high homocysteine levels can increase stroke risk.
FAQ About the Stroke Concept Map
Who can benefit from using this template?
Anyone interested in understanding stroke, including patients, caregivers, and individuals concerned about their heart health.
What information should be included in the concept map?
Definition of stroke, types (ischemic, hemorrhagic), symptoms (FAST), causes (blood clot, bleeding), risk factors (blood pressure, diabetes), complications (paralysis, speech problems), prevention tips (healthy lifestyle), treatment options (clot-busting drugs, surgery).
Can I customize this template?
Absolutely! This is a flexible tool. Adapt it to include specific details relevant to your situation or area of interest.
Free Download Your Concept Map Template Today!
Empower yourself with knowledge! Download our FREE template today and unlock the power of visual learning. Click the Use Template button on this page to access this valuable resource.
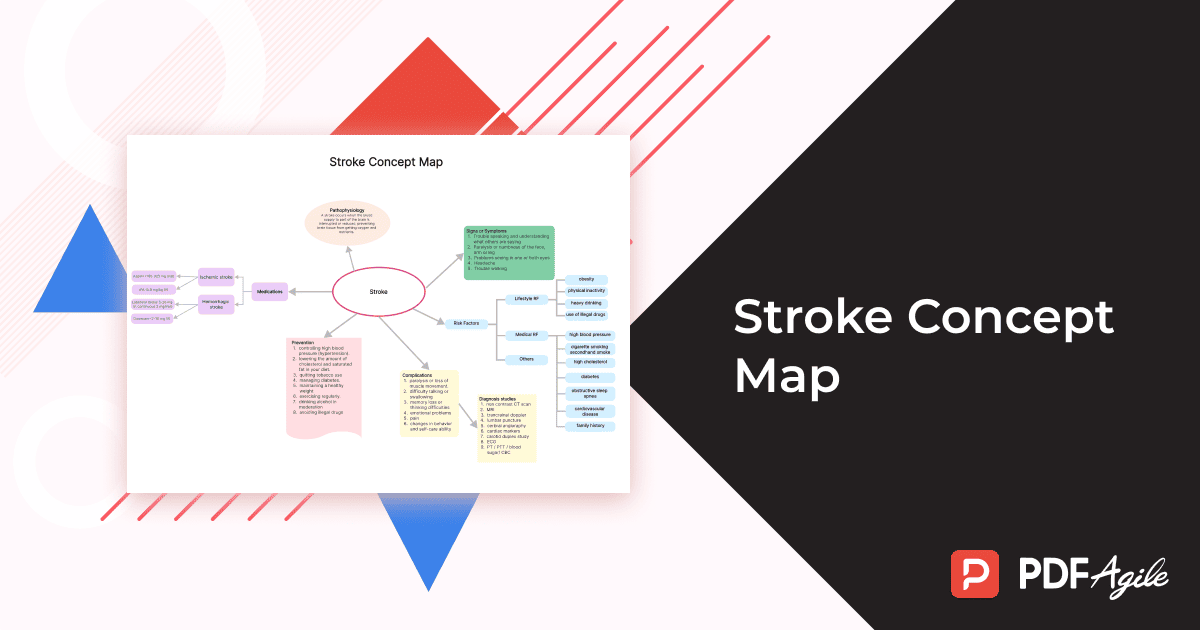
Visualize, Understand, Prevent Stroke
Stroke concept maps empower both patients and healthcare professionals to understand, prevent, and potentially improve recovery outcomes from stroke. Download your free template and start visualizing a healthier future for your brain!