The business world is full of innovation, and understanding how successful companies create and capture value is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs and existing businesses alike. This is where the Business Model Canvas (BMC) comes in.
What is the Business Model Canvas?
The BMC is a visual tool that helps businesses map out their core strategy and operations. It breaks down a business model into nine key building blocks:
- Customer Segments: Who are your target customers?
- Value Propositions: What unique value do you offer your customers?
- Channels: How do you reach your customers?
- Customer Relationships: How do you interact with your customers?
- Revenue Streams: How do you generate revenue?
- Key Resources: What resources are essential for your business?
- Key Activities: What key activities are critical to your success?
- Key Partnerships: Who are your key partners?
- Cost Structure: What are the costs associated with running your business?
By analyzing these components, businesses can gain a holistic understanding of their operations and identify areas for improvement.
Learning from the Best: 12 Business Model Canvas Examples
Let's delve into the BMCs of some of the most successful companies across various industries:
1. Google Business Model Canvas (Search Engine & Online Advertising)
Google, founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, revolutionized how we access information online. Starting as a search engine, Google quickly became the dominant player due to its superior search algorithm. Today, Google's influence extends far beyond search, encompassing a vast ecosystem of products and services, including online advertising, cloud computing, software, and hardware. However, its core business model remains centered around organizing the world's information and making it universally accessible and useful, primarily monetized through online advertising.
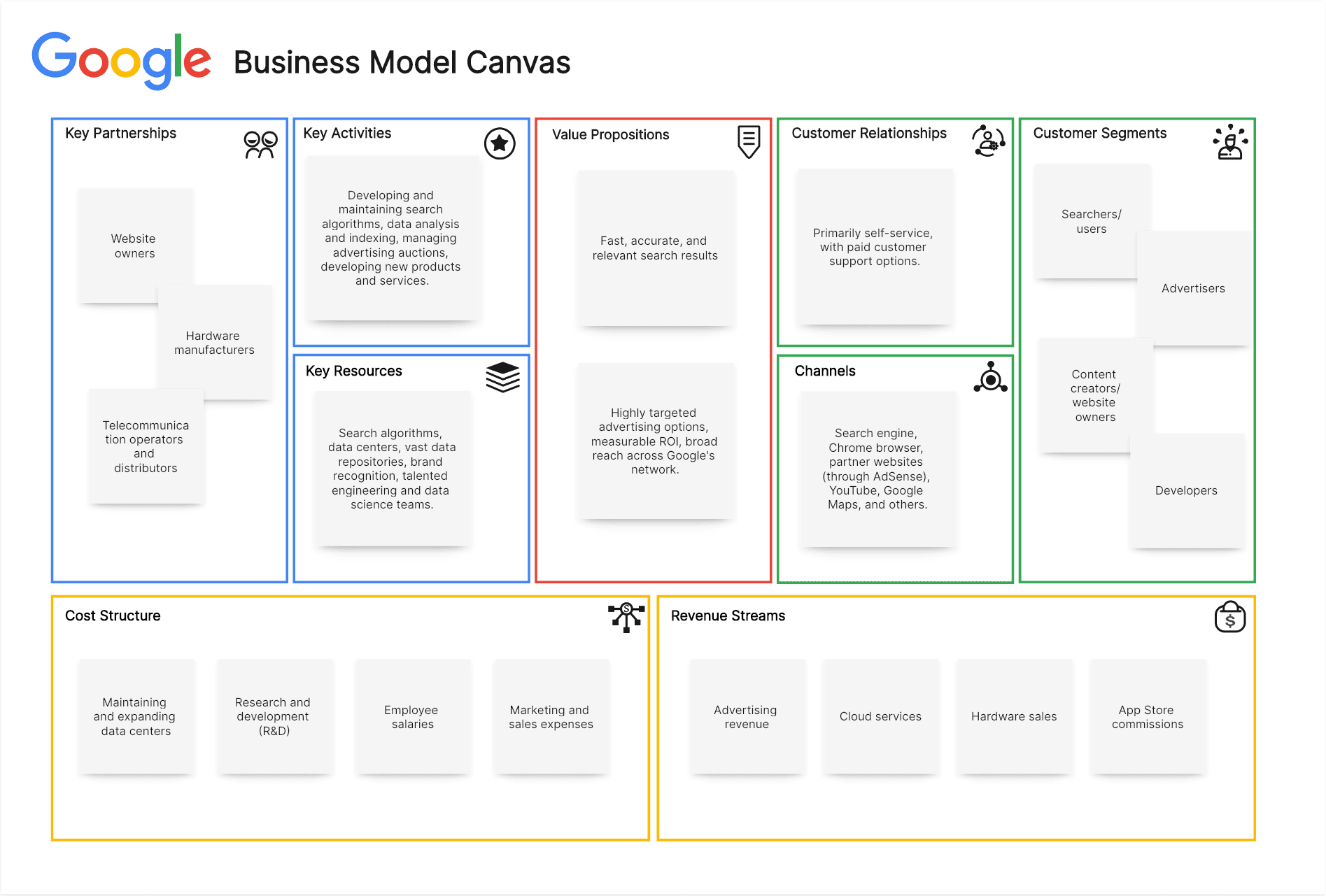
Google Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Searchers/Users: Individuals worldwide seeking information, answers, and resources online, across various demographics and interests.
Advertisers: Businesses of all sizes (from small local businesses to large multinational corporations) seeking to reach their target audience through online advertising.
Content Creators/Website Owners: Individuals and organizations creating content online and seeking to monetize their websites through advertising.
Developers: Creating applications and services that integrate with Google's platforms and APIs.
Value Propositions:
Searchers/Users: Fast, accurate, and relevant search results, access to a vast repository of information, free access to a world of knowledge, and a user-friendly interface.
Advertisers: Highly targeted advertising options based on keywords, demographics, interests, and location; measurable ROI through detailed analytics; broad reach across Google's search engine, partner websites (AdSense network), and YouTube; and various ad formats (text, display, video).
Content Creators/Website Owners: Opportunity to monetize their websites and content through AdSense, access to Google's advertising technology and infrastructure, and increased website traffic through search engine optimization (SEO).
Developers: Access to powerful APIs and tools, a large user base to reach, and opportunities for monetization through app store commissions and other integrations.
Channels:
Search engine, mobile app (Google Search), Chrome browser, partner websites (through AdSense), YouTube, Google Maps, and other Google products and services.
Customer Relationships:
Primarily self-service through online tools and resources. Paid support options are available for advertisers through Google Ads support. Community forums and online documentation provide additional support for users and developers.
Revenue Streams:
Advertising Revenue (Dominant): Primarily through Google Ads, including:
- Search Advertising: Text ads displayed alongside search results.
- Display Advertising: Banner and other visual ads displayed on websites within the AdSense network.
- YouTube Advertising: Video ads displayed before, during, or after YouTube videos.
Other Revenue Streams:
- Cloud Services (Google Cloud Platform - GCP): Providing cloud computing infrastructure, storage, and other services to businesses.
- Hardware Sales: Pixel phones, Nest smart home devices, and other hardware products.
- App Store Commissions (Google Play Store): Taking a percentage of revenue from app sales and in-app purchases.
- Licensing and other partnerships.
Key Resources:
Search algorithms (PageRank and others), data centers (massive infrastructure for storing and processing data), vast data repositories, brand recognition, talented engineering and data science teams, and a global network of servers and infrastructure.
Key Activities:
Developing and maintaining search algorithms, data analysis and indexing of web pages, managing advertising auctions and serving ads, developing new products and services (Gmail, Maps, YouTube, etc.), and investing in research and development.
Key Partnerships:
Website owners participating in the Google AdSense program, hardware manufacturers (for Pixel and other devices), telecommunication companies, mobile carriers, and various technology partners.
Cost Structure:
Maintaining and expanding data centers (a significant cost), research and development (R&D), employee salaries (especially engineers and data scientists), marketing and sales expenses, and bandwidth and network infrastructure costs.
Insights:
- Google's success is largely attributed to its superior search algorithm, which provides highly relevant results to users, creating a strong user base.
- The AdSense program allows Google to extend its advertising reach to millions of websites, creating a powerful network effect and significantly expanding its advertising inventory.
- Continuous investment in R&D keeps Google at the forefront of search technology, artificial intelligence, and other fields, allowing it to expand into new markets and product categories.
- The focus on a free search service for users created a massive user base, which is crucial for the advertising-based business model.
- Data is at the core of Google's business, driving both search relevance and targeted advertising.
2. Tesla Business Model Canvas (Automobile)
Tesla, Inc., founded in 2003 by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning and later led by visionary entrepreneur Elon Musk, set out to prove that electric vehicles (EVs) could be better, quicker, and more fun to drive than gasoline cars. With a mission to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy, Tesla has become synonymous with innovation in the automotive and energy sectors. Beyond producing electric cars that defy traditional performance metrics, Tesla has expanded its product line to include solar energy products and energy storage solutions, challenging the automotive industry's status quo and leading the charge toward a more sustainable future.
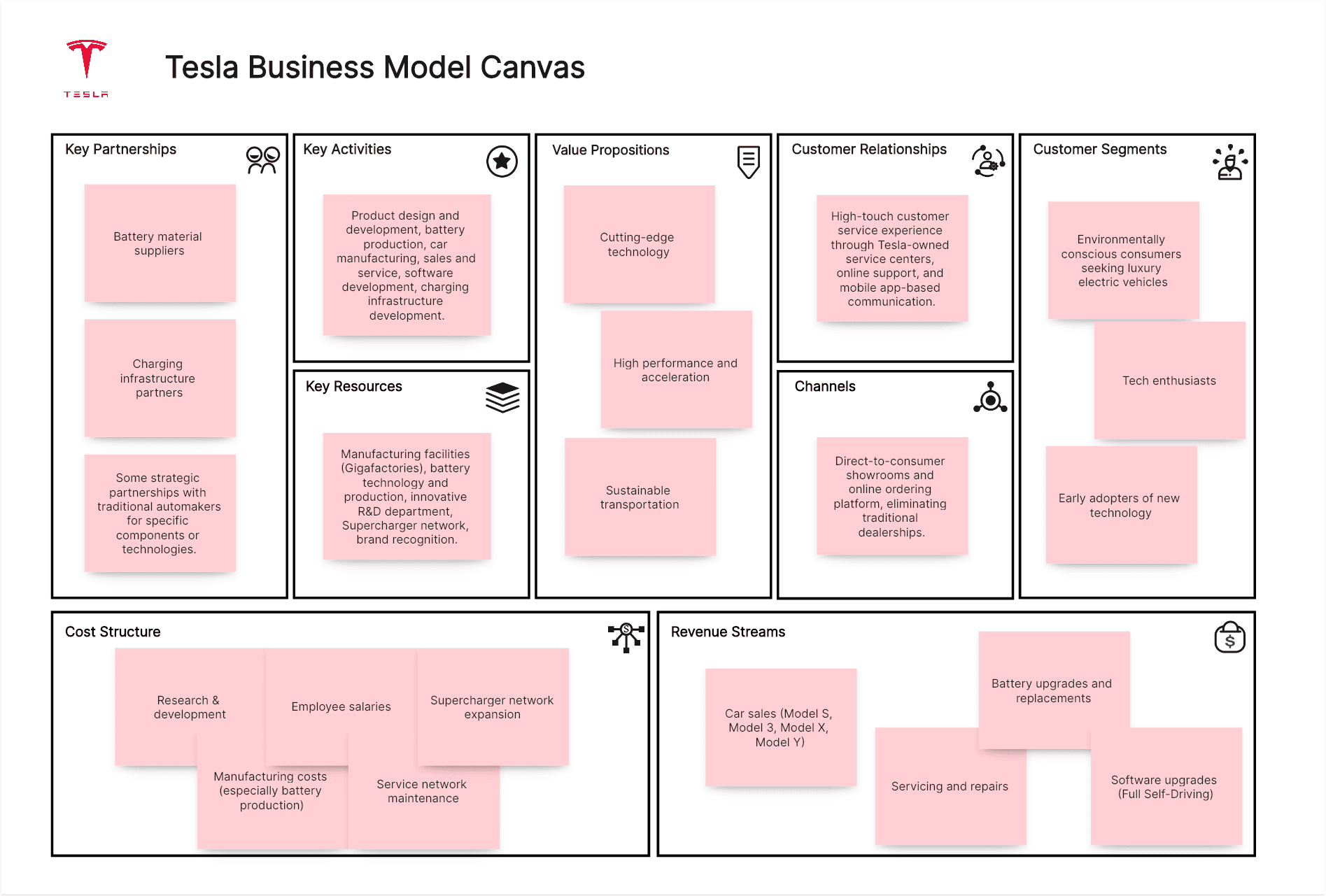
Tesla Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Environmentally conscious consumers seeking luxury electric vehicles, tech enthusiasts, early adopters of new technology, and increasingly, mainstream consumers looking for efficient and performance-oriented vehicles.
Value Propositions:
Cutting-edge technology (battery technology, autonomous driving features), high performance and acceleration, sustainable transportation, over-the-air software updates, a seamless and integrated user experience.
Channels:
Direct-to-consumer showrooms and online ordering platform, eliminating traditional dealerships.
Customer Relationships:
High-touch customer service experience through Tesla-owned service centers, online support, and mobile app-based communication.
Revenue Streams:
Car sales (Model S, Model 3, Model X, Model Y), servicing and repairs, battery upgrades and replacements, software upgrades (Full Self-Driving), energy storage products (Powerwall, Powerpack), and solar energy products.
Key Resources:
Manufacturing facilities (Gigafactories), battery technology and production, innovative R&D department, Supercharger network, brand recognition.
Key Activities:
Product design and development, battery production, car manufacturing, sales and service, software development, charging infrastructure development.
Key Partnerships:
Battery material suppliers, charging infrastructure partners, some strategic partnerships with traditional automakers for specific components or technologies.
Cost Structure:
Research & development, manufacturing costs (especially battery production), employee salaries, service network maintenance, Supercharger network expansion.
Insights:
- Direct sales eliminated intermediaries, fostering a closer relationship with customers and controlling the customer experience.
- Continuous investment in R&D ensured their technology leadership in the EV market, particularly in battery technology and autonomous driving.
- Their commitment to sustainability resonated with growing consumer environmental consciousness, creating a strong brand identity.
- The Supercharger network provides a crucial advantage by addressing range anxiety and enabling long-distance travel.
3. McDonald’s Business Model Canvas (Food)
McDonald's, founded in 1940, is the world's largest restaurant chain by revenue, serving millions of customers daily. Known for its standardized menu, fast service, and affordable prices, McDonald's has become a global icon of fast food. The company's business model is built on a franchise system, allowing for rapid expansion and consistent quality control across its vast network of restaurants.
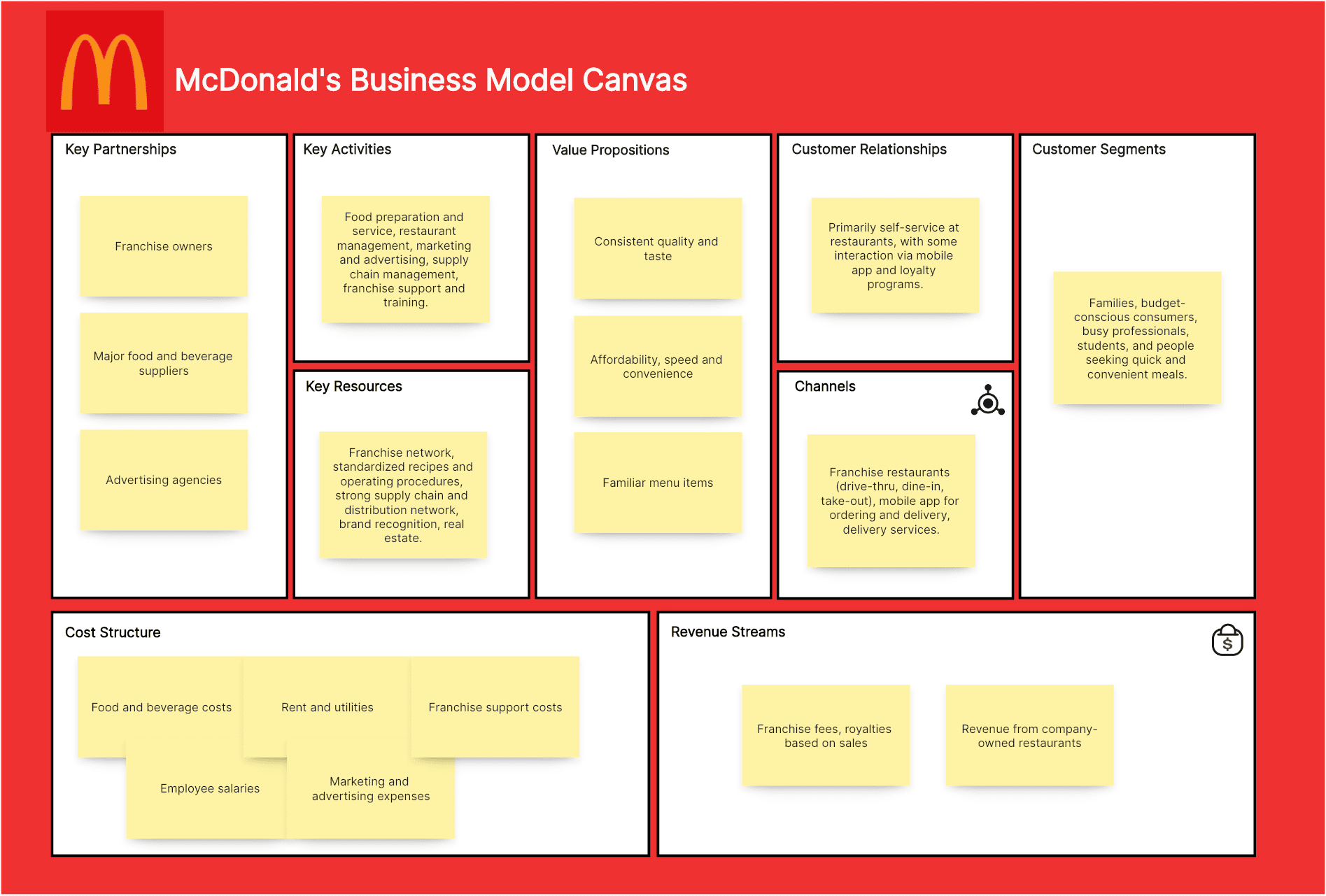
McDonald's Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Families, budget-conscious consumers, busy professionals, students, and people seeking quick and convenient meals.
Value Propositions:
Consistent quality and taste, affordability, speed and convenience, familiar menu items, recognizable brand.
Channels:
Franchise restaurants (drive-thru, dine-in, take-out), mobile app for ordering and delivery, delivery services (partnerships with third-party delivery platforms).
Customer Relationships:
Primarily self-service at restaurants, with some interaction via mobile app and loyalty programs.
Revenue Streams:
Franchise fees, royalties based on sales, and revenue from company-owned restaurants.
Key Resources:
Franchise network, standardized recipes and operating procedures, strong supply chain and distribution network, brand recognition, real estate.
Key Activities:
Food preparation and service, restaurant management, marketing and advertising, supply chain management, franchise support and training.
Key Partnerships:
Franchise owners, major food and beverage suppliers, advertising agencies, technology providers.
Cost Structure:
Food and beverage costs, employee salaries, rent and utilities, marketing and advertising expenses, franchise support costs.
Insights:
- The franchise model allows for rapid expansion with minimal capital investment from the parent company.
- Standardized recipes and operating procedures ensure consistent quality and efficiency across all locations.
- Strong supply chain management enables cost control and efficient distribution of ingredients.
- Extensive marketing and advertising campaigns maintain brand awareness and drive customer traffic.
4. Apple Business Model Canvas (Consumer Electronics)
Apple Inc., founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, is a global technology giant known for its innovative consumer electronics, software, and online services. Apple's focus on design, user experience, and a tightly integrated ecosystem has cultivated a loyal customer base and established the company as a premium brand in the technology industry.
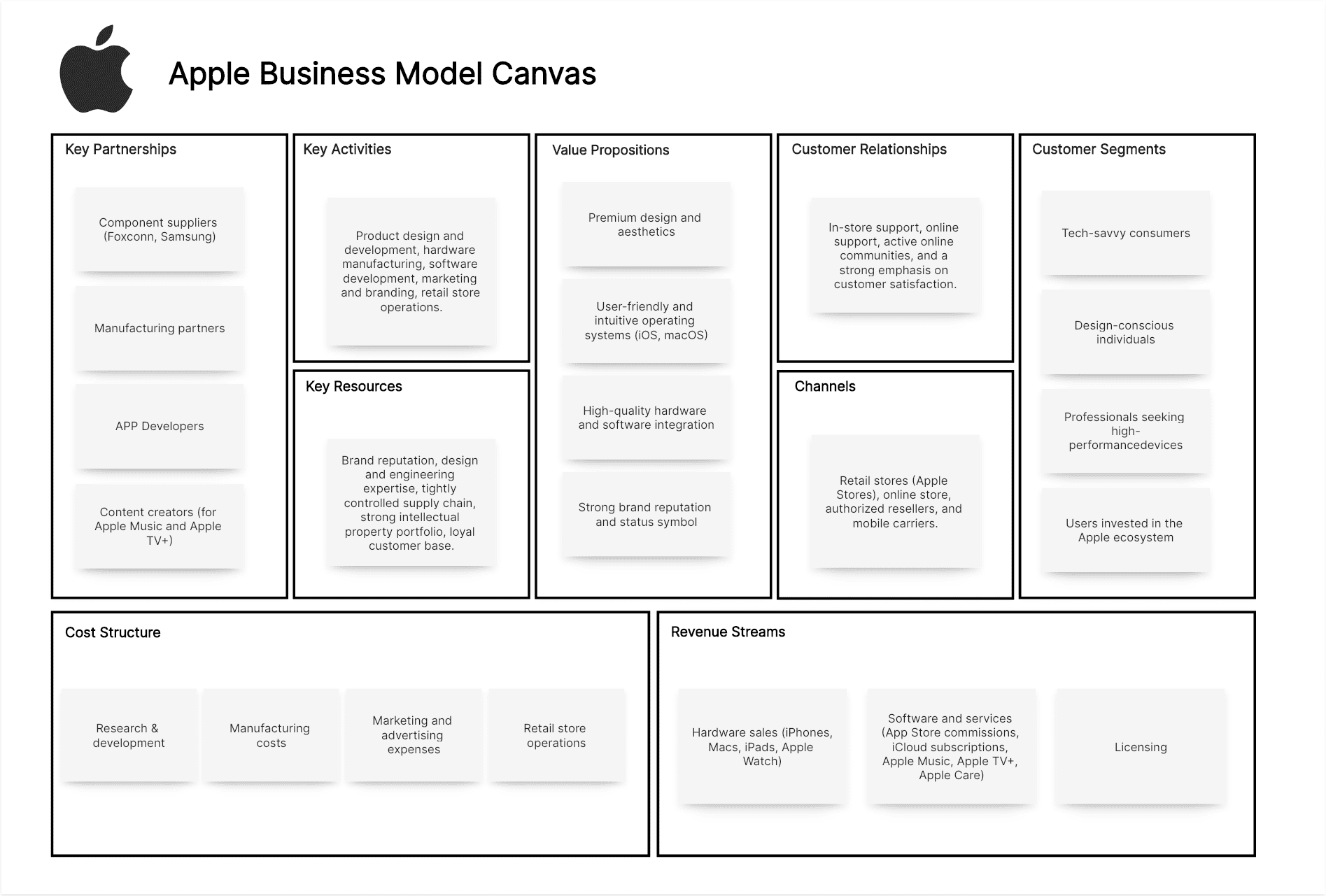
Apple Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Tech-savvy consumers, design-conscious individuals, professionals seeking high-performance devices, and users invested in the Apple ecosystem.
Value Propositions:
Premium design and aesthetics, user-friendly and intuitive operating systems (iOS, macOS), high-quality hardware and software integration, a seamless and integrated ecosystem of devices and services, strong brand reputation and status symbol.
Channels:
Retail stores (Apple Stores), online store, authorized resellers, and mobile carriers.
Customer Relationships:
In-store support (Genius Bar), online support, active online communities, and a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction.
Revenue Streams:
Hardware sales (iPhones, Macs, iPads, Apple Watch), software and services (App Store commissions, iCloud subscriptions, Apple Music, Apple TV+, Apple Care), and licensing.
Key Resources:
Brand reputation, design and engineering expertise, tightly controlled supply chain, strong intellectual property portfolio, loyal customer base.
Key Activities:
Product design and development, hardware manufacturing (outsourced but tightly controlled), software development, marketing and branding, retail store operations.
Key Partnerships:
Component suppliers (Foxconn, Samsung), manufacturing partners, app developers, content creators (for Apple Music and Apple TV+), and mobile carriers.
Cost Structure:
Research & development, manufacturing costs, marketing and advertising expenses, retail store operations, content acquisition (for Apple Music and Apple TV+).
Insights:
- The tightly integrated ecosystem of hardware, software, and services creates customer lock-in and encourages repeat purchases.
- The focus on design and user experience differentiates Apple products from competitors and justifies premium pricing.
- A strong brand reputation and effective marketing contribute to high customer loyalty and brand advocacy.
- The App Store provides a significant revenue stream through commissions and fosters a thriving developer community.
5. Meta (Facebook) Business Model Canvas (Social Media)
Meta, formerly known as Facebook, was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg and his college roommates. It has become the world's largest social networking platform, connecting billions of people globally. Beyond its core social networking service, Meta has expanded its portfolio to include other popular platforms like Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus VR, creating a vast ecosystem of social and communication tools. Its business model primarily revolves around connecting users and monetizing their engagement through targeted advertising.
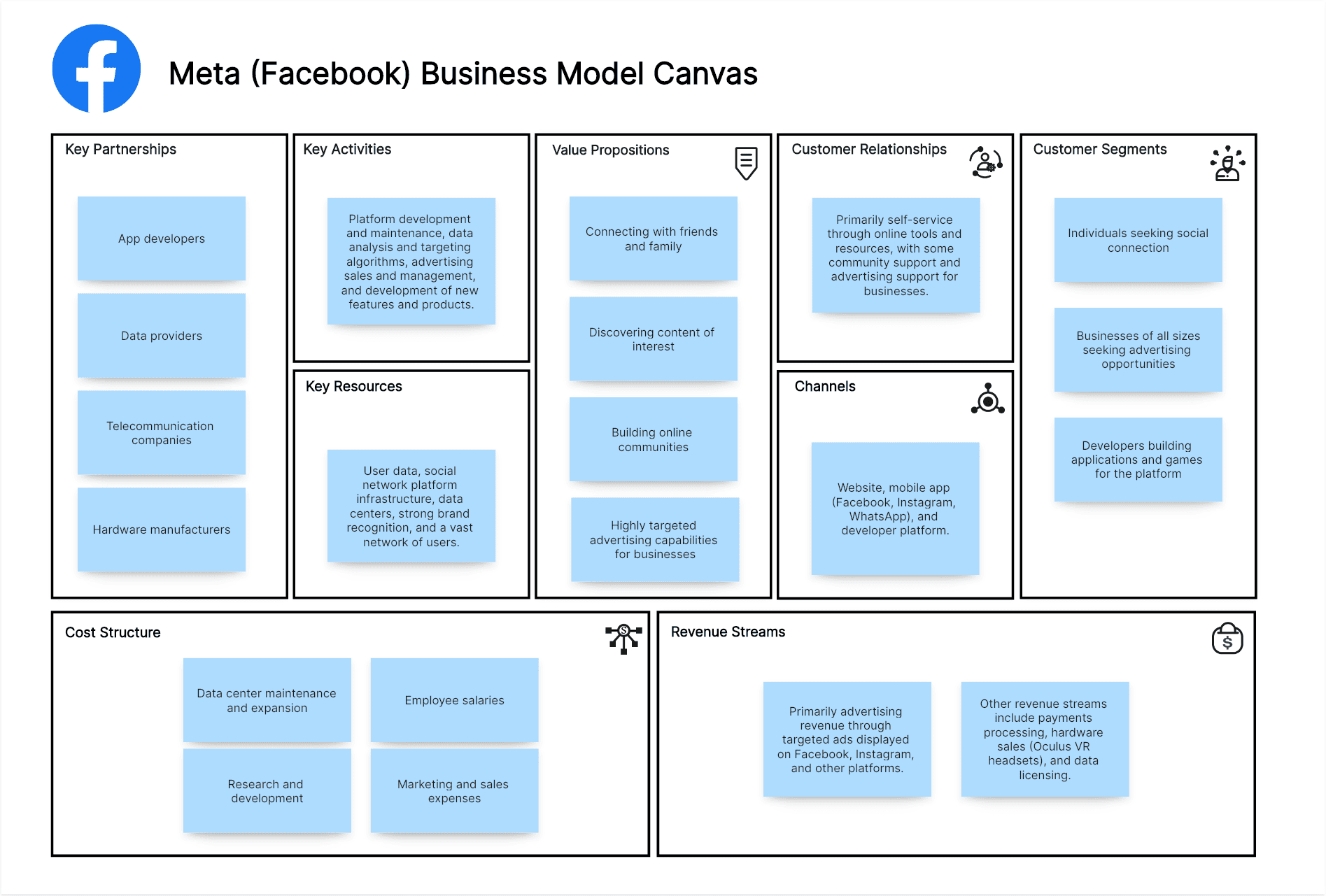
Meta (Facebook) Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Individuals seeking social connection, businesses of all sizes seeking advertising opportunities, and developers building applications and games for the platform.
Value Propositions:
Connecting with friends and family, discovering content of interest, building online communities, highly targeted advertising capabilities for businesses, and a platform for developers to reach a vast audience.
Channels:
Website, mobile app (Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp), and developer platform.
Customer Relationships:
Primarily self-service through online tools and resources, with some community support and advertising support for businesses.
Revenue Streams:
Primarily advertising revenue through targeted ads displayed on Facebook, Instagram, and other platforms. Other revenue streams include payments processing, hardware sales (Oculus VR headsets), and data licensing.
Key Resources:
User data, social network platform infrastructure, data centers, strong brand recognition, and a vast network of users.
Key Activities:
Platform development and maintenance, data analysis and targeting algorithms, advertising sales and management, and development of new features and products.
Key Partnerships:
App developers, data providers, telecommunication companies, and hardware manufacturers.
Cost Structure:
Data center maintenance and expansion, research and development, employee salaries, and marketing and sales expenses.
Insights:
- The massive user base creates a powerful network effect, making the platform more valuable as more people join.
- Sophisticated data analysis and targeting algorithms enable highly effective advertising for businesses.
- Acquisitions of other popular platforms like Instagram and WhatsApp have expanded Meta's reach and diversified its revenue streams.
- Concerns about data privacy and user trust have become significant challenges for the company.
6. Amazon Business Model Canvas (E-Commerce)
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, started as an online bookstore and has since transformed into the world's largest e-commerce marketplace and a leading provider of cloud computing services. Amazon's business model is characterized by its vast product selection, competitive pricing, convenient delivery options, and a strong focus on customer satisfaction.
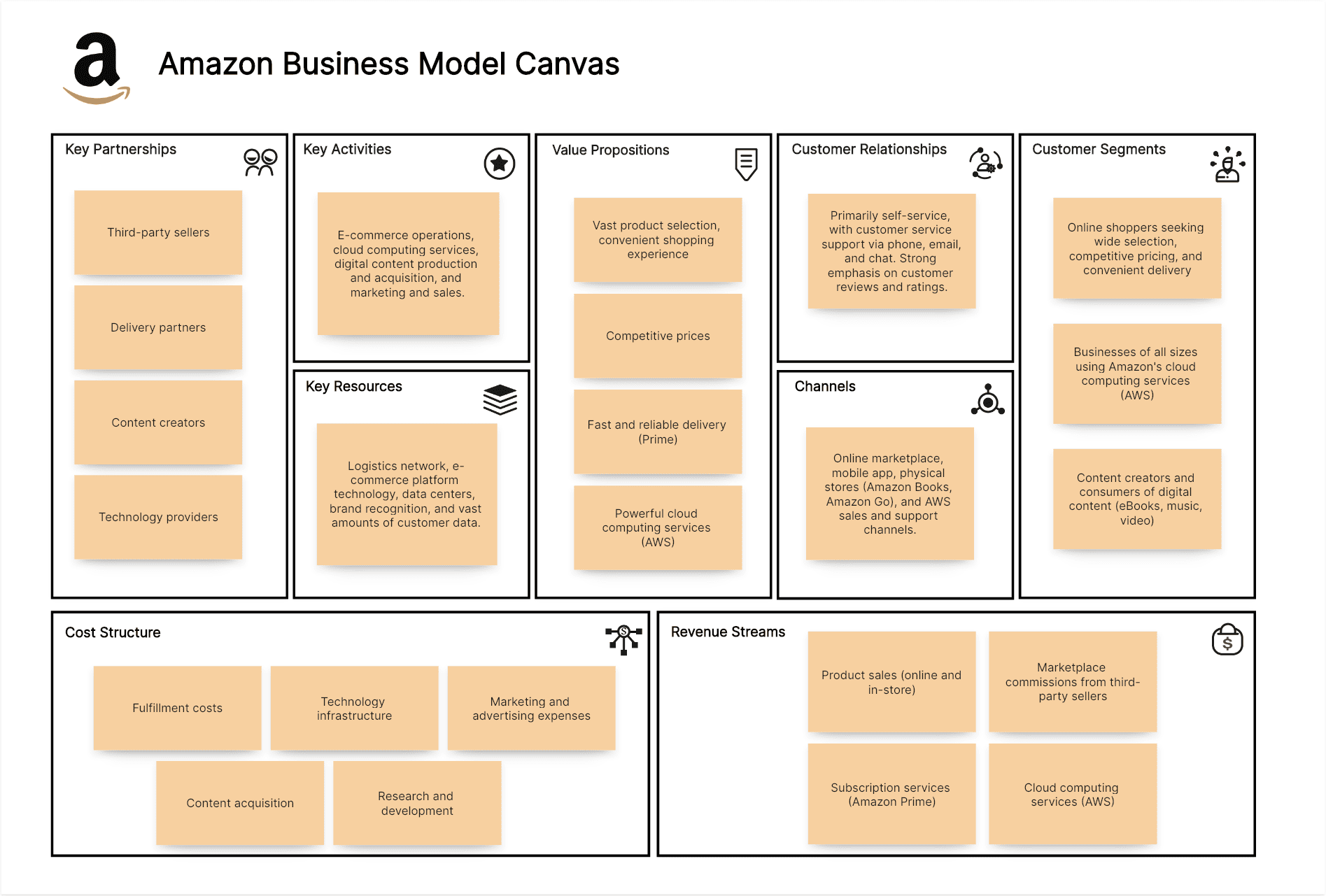
Amazon Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Online shoppers seeking wide selection, competitive pricing, and convenient delivery; businesses of all sizes using Amazon's cloud computing services (AWS); and content creators and consumers of digital content (eBooks, music, video).
Value Propositions:
Vast product selection, competitive prices, fast and reliable delivery (Prime), convenient shopping experience, powerful cloud computing services (AWS), and a diverse range of digital content.
Channels:
Online marketplace, mobile app, physical stores (Amazon Books, Amazon Go), and AWS sales and support channels.
Customer Relationships:
Primarily self-service, with customer service support via phone, email, and chat. Strong emphasis on customer reviews and ratings.
Revenue Streams:
Product sales (online and in-store), marketplace commissions from third-party sellers, subscription services (Amazon Prime), cloud computing services (AWS), advertising, and digital content sales and rentals.
Key Resources:
Logistics network (fulfillment centers, delivery infrastructure), e-commerce platform technology, data centers (for AWS), brand recognition, and vast amounts of customer data.
Key Activities:
E-commerce operations (order fulfillment, logistics), cloud computing services (AWS infrastructure and development), digital content production and acquisition, and marketing and sales.
Key Partnerships:
Third-party sellers, delivery partners, content creators (authors, musicians, filmmakers), and technology providers.
Cost Structure:
Fulfillment costs (warehousing, shipping), technology infrastructure (data centers, servers), marketing and advertising expenses, content acquisition, and research and development.
Insights:
- The Amazon Prime subscription service drives customer loyalty and encourages repeat purchases.
- AWS has become a major revenue driver, providing highly profitable cloud computing services to businesses of all sizes.
- The vast logistics network and fulfillment centers enable fast and efficient delivery, a key competitive advantage.
- Amazon's data-driven approach allows for personalized recommendations and targeted marketing.
7. Uber Business Model Canvas (Taxi & Limousine Services and Ride-Sharing Services)
Uber, founded in 2009, revolutionized the transportation industry by introducing on-demand ride-sharing services through a mobile app. Uber's business model connects riders with drivers using a network-based platform, offering a convenient and often more affordable alternative to traditional taxis.
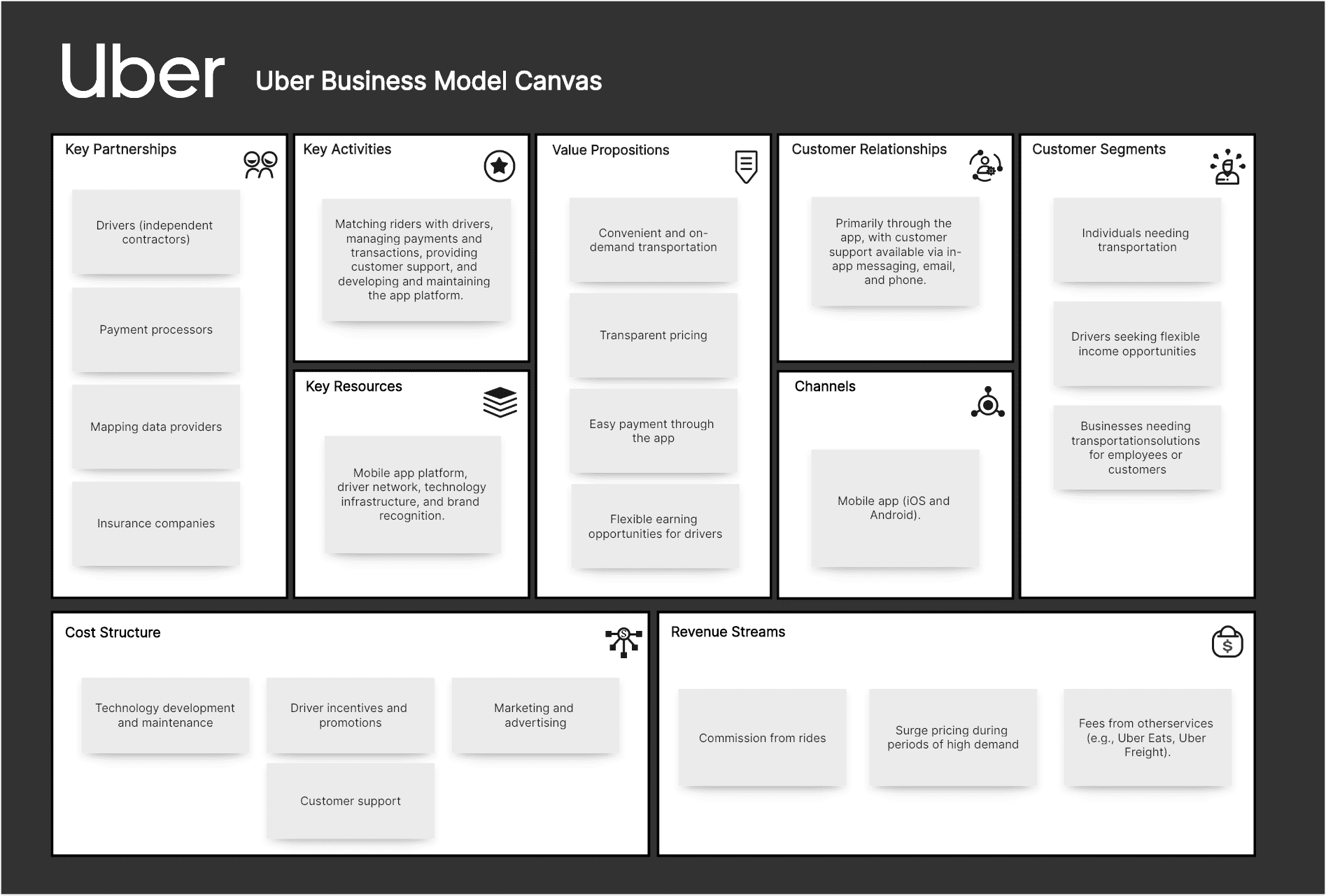
Uber Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Individuals needing transportation, drivers seeking flexible income opportunities, and businesses needing transportation solutions for employees or customers.
Value Propositions:
Convenient and on-demand transportation, transparent pricing, easy payment through the app, flexible earning opportunities for drivers, and a wide range of ride options (e.g., UberX, Uber Black, Uber Pool).
Channels:
Mobile app (iOS and Android).
Customer Relationships:
Primarily through the app, with customer support available via in-app messaging, email, and phone.
Revenue Streams:
Commission from rides (a percentage of each fare), surge pricing during periods of high demand, and fees from other services (e.g., Uber Eats, Uber Freight).
Key Resources:
Mobile app platform, driver network, technology infrastructure (servers, mapping technology), and brand recognition.
Key Activities:
Matching riders with drivers, managing payments and transactions, providing customer support, and developing and maintaining the app platform.
Key Partnerships:
Drivers (independent contractors), payment processors, mapping data providers, and insurance companies.
Cost Structure:
Technology development and maintenance, driver incentives and promotions, customer support, marketing and advertising, and legal and regulatory compliance.
Insights:
- The network-based platform creates a marketplace that efficiently connects riders and drivers.
- Surge pricing allows Uber to balance supply and demand during peak hours.
- The reliance on independent contractors (drivers) allows Uber to avoid many traditional employment costs.
- Regulatory challenges and competition from other ride-sharing services remain significant factors.
8. Spotify Business Model Canvas (Audio Streaming Services)
Spotify, founded in 2006, revolutionized the music industry by offering a legal and convenient way to stream music online. Its freemium business model, offering both free (ad-supported) and paid (ad-free) subscriptions, has made it the leading audio streaming service globally.
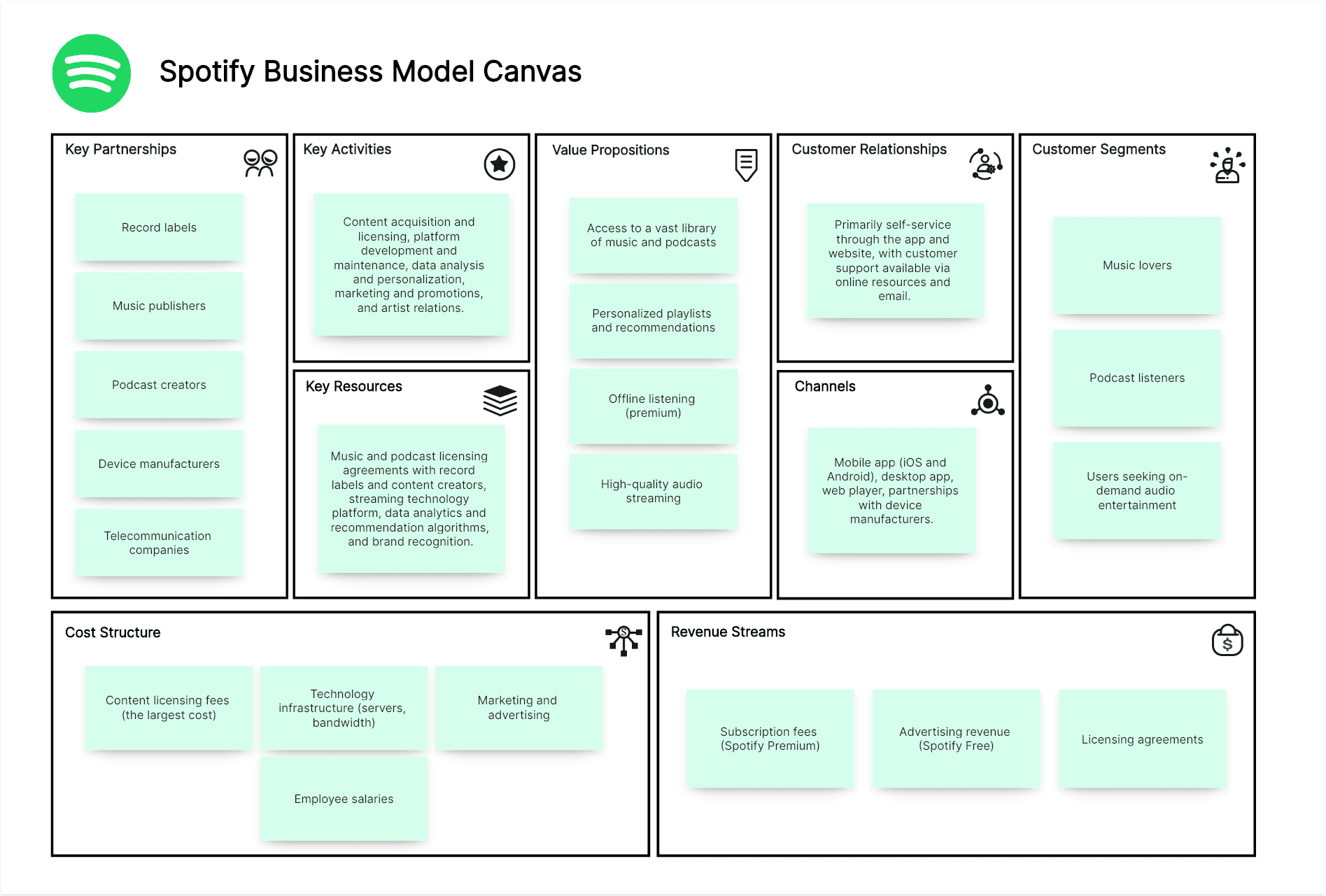
Spotify Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Music lovers, podcast listeners, and users seeking on-demand audio entertainment.
Value Propositions:
Access to a vast library of music and podcasts, personalized playlists and recommendations, offline listening (premium), high-quality audio streaming, and discovery of new artists and content.
Channels:
Mobile app (iOS and Android), desktop app, web player, partnerships with device manufacturers (smart speakers, gaming consoles).
Customer Relationships:
Primarily self-service through the app and website, with customer support available via online resources and email.
Revenue Streams:
Subscription fees (Spotify Premium), advertising revenue (Spotify Free), and licensing agreements.
Key Resources:
Music and podcast licensing agreements with record labels and content creators, streaming technology platform, data analytics and recommendation algorithms, and brand recognition.
Key Activities:
Content acquisition and licensing, platform development and maintenance, data analysis and personalization, marketing and promotions, and artist relations.
Key Partnerships:
Record labels, music publishers, podcast creators, device manufacturers, telecommunication companies, and social media platforms.
Cost Structure:
Content licensing fees (the largest cost), technology infrastructure (servers, bandwidth), research and development, marketing and advertising, and employee salaries.
Insights:
- The freemium model attracts a large user base, with a portion converting to paid subscriptions.
- Personalized playlists and recommendations enhance user engagement and retention.
- Licensing agreements with major record labels are crucial for maintaining a comprehensive music library.
- Competition from other streaming services and the power of record labels are ongoing challenges.
9. Netflix Business Model Canvas (Video Streaming Services)
Netflix, founded in 1997 as a DVD rental service, transitioned to online streaming in 2007 and has become the dominant force in the video streaming industry. Its subscription-based model provides users with on-demand access to a vast library of movies, TV shows, and original content.
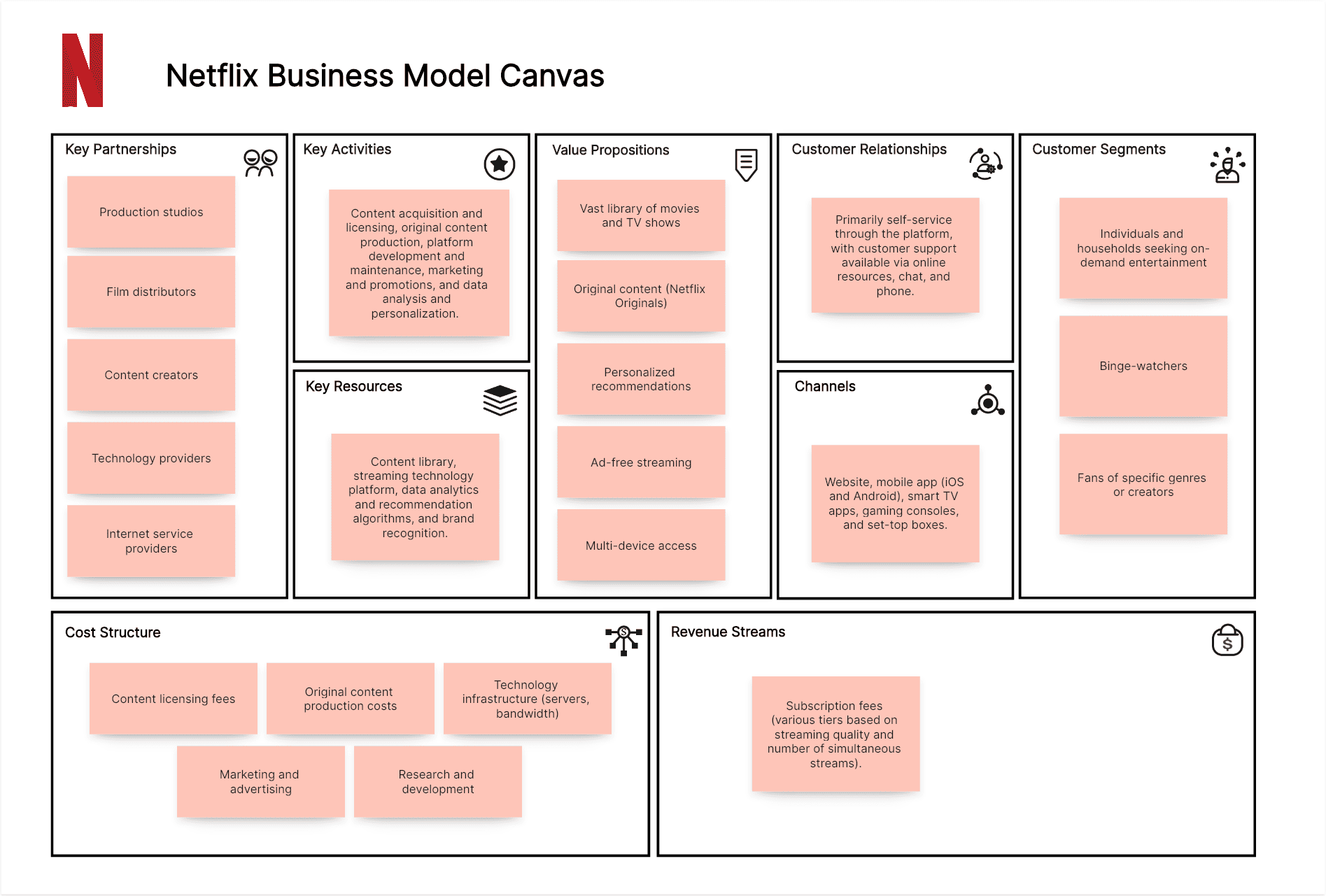
Netflix Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Individuals and households seeking on-demand entertainment, binge-watchers, and fans of specific genres or creators.
Value Propositions:
Vast library of movies and TV shows, original content (Netflix Originals), personalized recommendations, ad-free streaming, and multi-device access.
Channels:
Website, mobile app (iOS and Android), smart TV apps, gaming consoles, and set-top boxes.
Customer Relationships:
Primarily self-service through the platform, with customer support available via online resources, chat, and phone.
Revenue Streams:
Subscription fees (various tiers based on streaming quality and number of simultaneous streams).
Key Resources:
Content library (licensed and original), streaming technology platform, data analytics and recommendation algorithms, and brand recognition.
Key Activities:
Content acquisition and licensing, original content production, platform development and maintenance, marketing and promotions, and data analysis and personalization.
Key Partnerships:
Production studios, film distributors, content creators, technology providers, and internet service providers.
Cost Structure:
Content licensing fees (a significant cost), original content production costs, technology infrastructure (servers, bandwidth), marketing and advertising, and research and development.
Insights:
- Original content production has become a key differentiator, attracting subscribers and reducing reliance on licensed content.
- Personalized recommendations enhance user engagement and content discovery.
- Competition from other streaming services and the increasing cost of content acquisition are major challenges.
- Global expansion has been a key growth strategy for Netflix.
10. Zara Business Model Canvas (Fashion)
Zara, founded in 1975, is a Spanish apparel retailer known for its "fast fashion" business model. This model emphasizes rapidly responding to changing fashion trends by designing, manufacturing, and distributing new clothing quickly and efficiently.
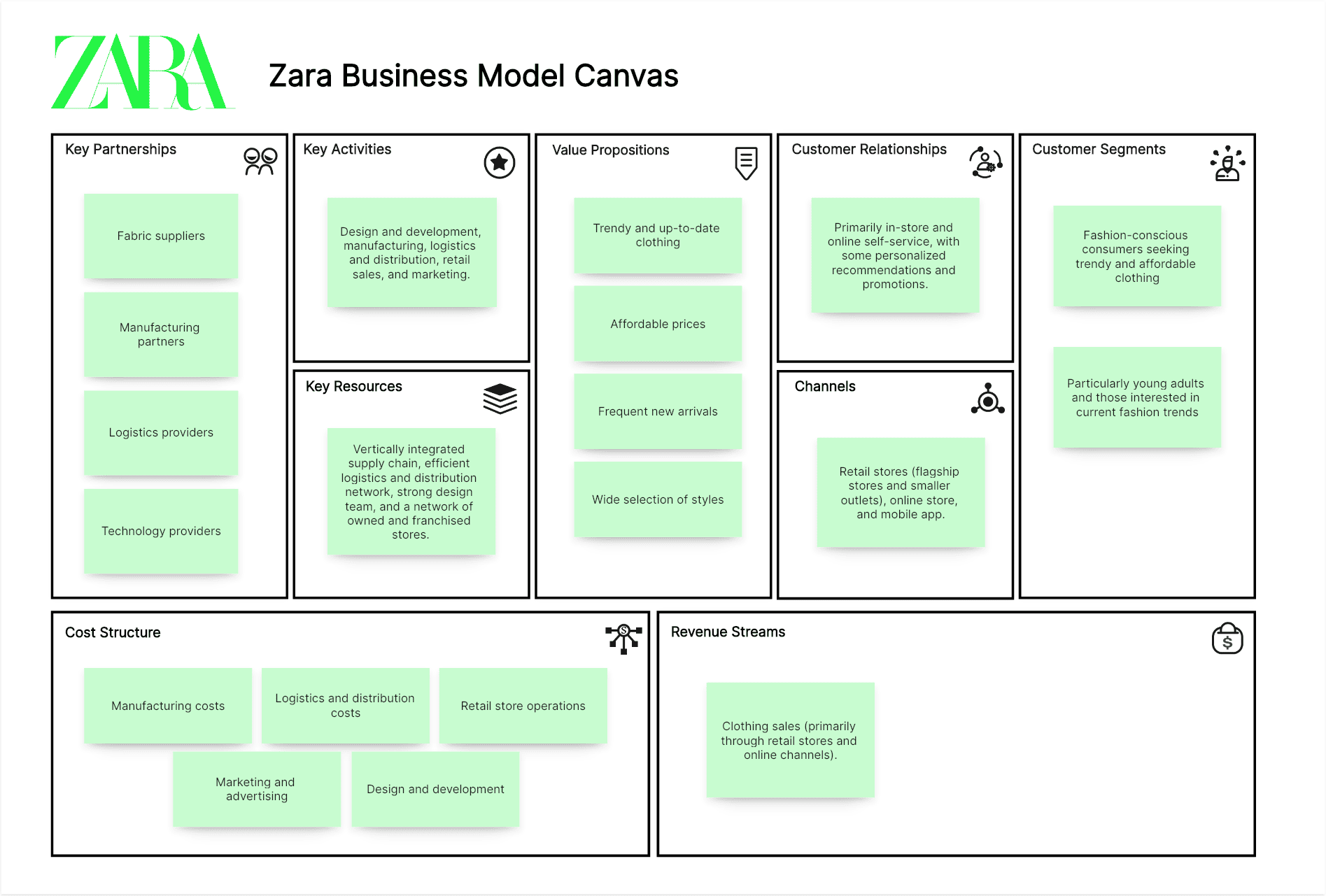
Zara Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Fashion-conscious consumers seeking trendy and affordable clothing, particularly young adults and those interested in current fashion trends.
Value Propositions:
Trendy and up-to-date clothing, affordable prices, frequent new arrivals, and a wide selection of styles.
Channels:
Retail stores (flagship stores and smaller outlets), online store, and mobile app.
Customer Relationships:
Primarily in-store and online self-service, with some personalized recommendations and promotions.
Revenue Streams:
Clothing sales (primarily through retail stores and online channels).
Key Resources:
Vertically integrated supply chain (design, manufacturing, distribution), efficient logistics and distribution network, strong design team, and a network of owned and franchised stores.
Key Activities:
Design and development, manufacturing (primarily in-house or through closely controlled suppliers), logistics and distribution, retail sales, and marketing.
Key Partnerships:
Fabric suppliers, manufacturing partners (some outsourced but closely managed), logistics providers, and technology providers.
Cost Structure:
Manufacturing costs (fabric, labor), logistics and distribution costs, retail store operations (rent, salaries), marketing and advertising, and design and development.
Insights:
- The vertically integrated supply chain enables rapid response to changing fashion trends and reduces lead times.
- Frequent new arrivals create a sense of urgency and encourage repeat purchases.
- Limited advertising and reliance on store locations in high-traffic areas contribute to cost efficiency.
- Maintaining quality control while producing large volumes of clothing at low cost is a key challenge.
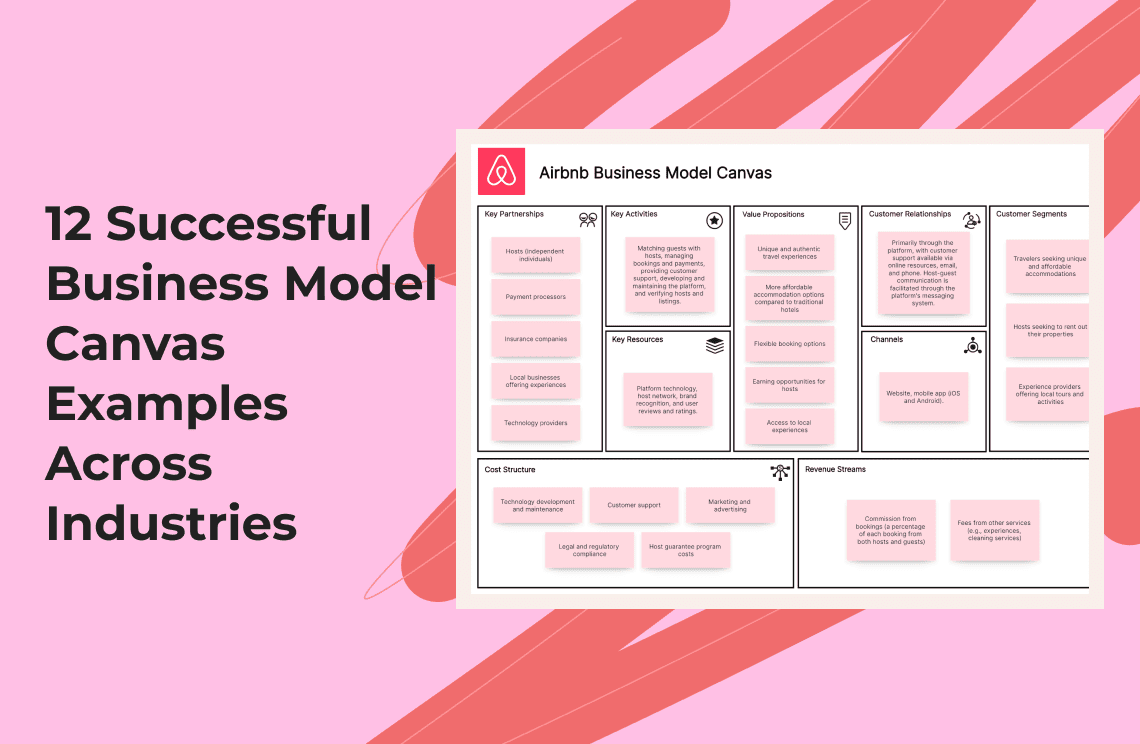
11. Airbnb Business Model Canvas (Hospitality)
Airbnb, founded in 2008, disrupted the traditional hospitality industry by creating an online marketplace that connects travelers with hosts who offer unique accommodations, ranging from apartments and houses to castles and treehouses. This peer-to-peer model provides travelers with more diverse and often more affordable lodging options while allowing hosts to earn income from their unused space.
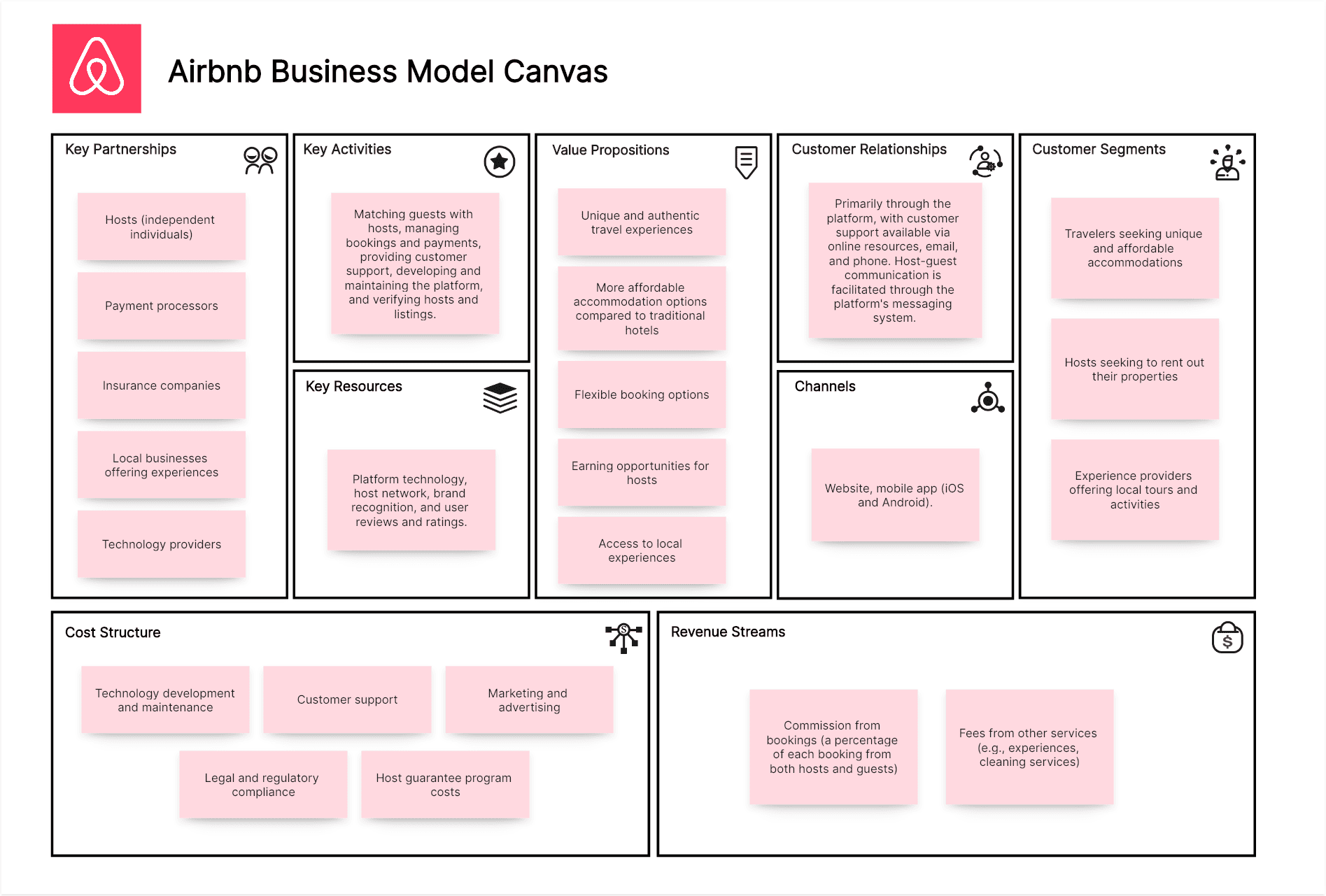
Airbnb Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Travelers seeking unique and affordable accommodations, hosts seeking to rent out their properties, and experience providers offering local tours and activities.
Value Propositions:
Unique and authentic travel experiences, more affordable accommodation options compared to traditional hotels, flexible booking options, earning opportunities for hosts, and access to local experiences.
Channels:
Website, mobile app (iOS and Android).
Customer Relationships:
Primarily through the platform, with customer support available via online resources, email, and phone. Host-guest communication is facilitated through the platform's messaging system.
Revenue Streams:
Commission from bookings (a percentage of each booking from both hosts and guests), and fees from other services (e.g., experiences, cleaning services).
Key Resources:
Platform technology (website and mobile app), host network, brand recognition, and user reviews and ratings.
Key Activities:
Matching guests with hosts, managing bookings and payments, providing customer support, developing and maintaining the platform, and verifying hosts and listings.
Key Partnerships:
Hosts (independent individuals), payment processors, insurance companies, local businesses offering experiences, and technology providers.
Cost Structure:
Technology development and maintenance, customer support, marketing and advertising, legal and regulatory compliance, and host guarantee program costs.
Insights:
- The peer-to-peer model allows for a vast inventory of diverse accommodations without Airbnb owning any properties.
- User reviews and ratings build trust and transparency within the marketplace.
- The platform creates a network effect, becoming more valuable as more hosts and guests join.
- Regulatory challenges and concerns about safety and security remain ongoing issues.
12. Starbucks Business Model Canvas (Coffee)
Starbucks, founded in 1971, transformed the coffee shop experience by creating a "third place" between home and work where people could socialize and enjoy high-quality coffee. The company's focus on creating a welcoming atmosphere, providing consistent quality, and offering a wide range of beverages and food items has made it a global coffeehouse giant.
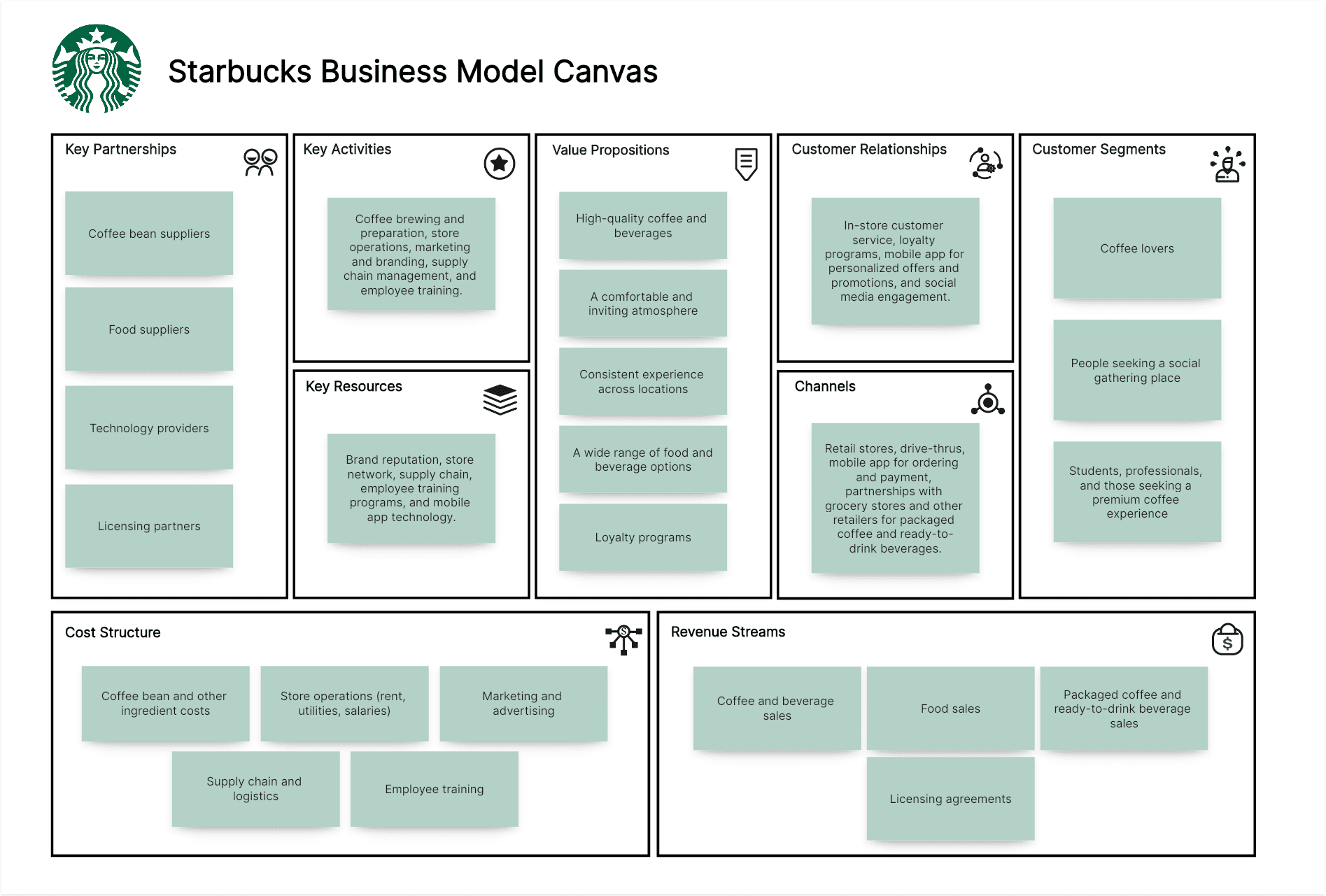
Starbucks Business Model Canvas Example:
Customer Segments:
Coffee lovers, people seeking a social gathering place, students, professionals, and those seeking a premium coffee experience.
Value Propositions:
High-quality coffee and beverages, a comfortable and inviting atmosphere ("third place"), consistent experience across locations, a wide range of food and beverage options, and loyalty programs.
Channels:
Retail stores (company-owned and licensed), drive-thrus, mobile app for ordering and payment, partnerships with grocery stores and other retailers for packaged coffee and ready-to-drink beverages.
Customer Relationships:
In-store customer service (baristas), loyalty programs (Starbucks Rewards), mobile app for personalized offers and promotions, and social media engagement.
Revenue Streams:
Coffee and beverage sales, food sales, packaged coffee and ready-to-drink beverage sales, and licensing agreements.
Key Resources:
Brand reputation, store network (physical locations), supply chain (coffee beans, other ingredients), employee training programs, and mobile app technology.
Key Activities:
Coffee brewing and preparation, store operations, marketing and branding, supply chain management, and employee training.
Key Partnerships:
Coffee bean suppliers, food suppliers, technology providers, and licensing partners.
Cost Structure:
Coffee bean and other ingredient costs, store operations (rent, utilities, salaries), marketing and advertising, supply chain and logistics, and employee training.
Insights:
- The "third place" concept creates a strong brand identity and fosters customer loyalty.
- Consistent quality and service across locations ensure a predictable and positive customer experience.
- Loyalty programs and mobile app features enhance customer engagement and drive repeat business.
- Competition from other coffee shops and the fluctuating price of coffee beans are ongoing challenges.
Get Started with Your Business Model Canvas
Now that you've seen how established companies like Meta (Facebook), Amazon, Uber, and others leverage the Business Model Canvas (BMC) to achieve success, it's your turn to put it into action!
Download our free Business Model Canvas Template from PDF Agile and customize it to create your own:
Link to PDF Agile Business Model Canvas Template
By mapping out your own business model, you can gain valuable insights and make informed decisions about your target market, value proposition, and overall business strategy. Remember, the best business models are constantly evolving. Use the BMC as a living document to track your progress, test assumptions, and refine your strategy as your business grows.
Bonus! Download All 12 Business Model Canvas Examples in PDF Format
Want to see more in-depth examples? Get a downloadable PDF containing all 12 Business Model Canvas examples explored in this article, allowing you to further dissect and customize them using PDF Agile:
Link to downloadable PDF with all 12 BMC examples
With these resources, you're well on your way to developing a winning business model for your own venture!