Superscript is a formatting style in which text is set slightly above the normal line of type. It is often used in mathematical expressions, chemical formulas, and citations. This feature adds clarity and precision to documents, making it essential for academic, scientific, and professional writing. Microsoft Word offers multiple ways to apply superscript, enhancing its versatility. Whether using the superscript button, keyboard shortcuts, or the font dialog box, creating superscript text in Word is both simple and efficient.
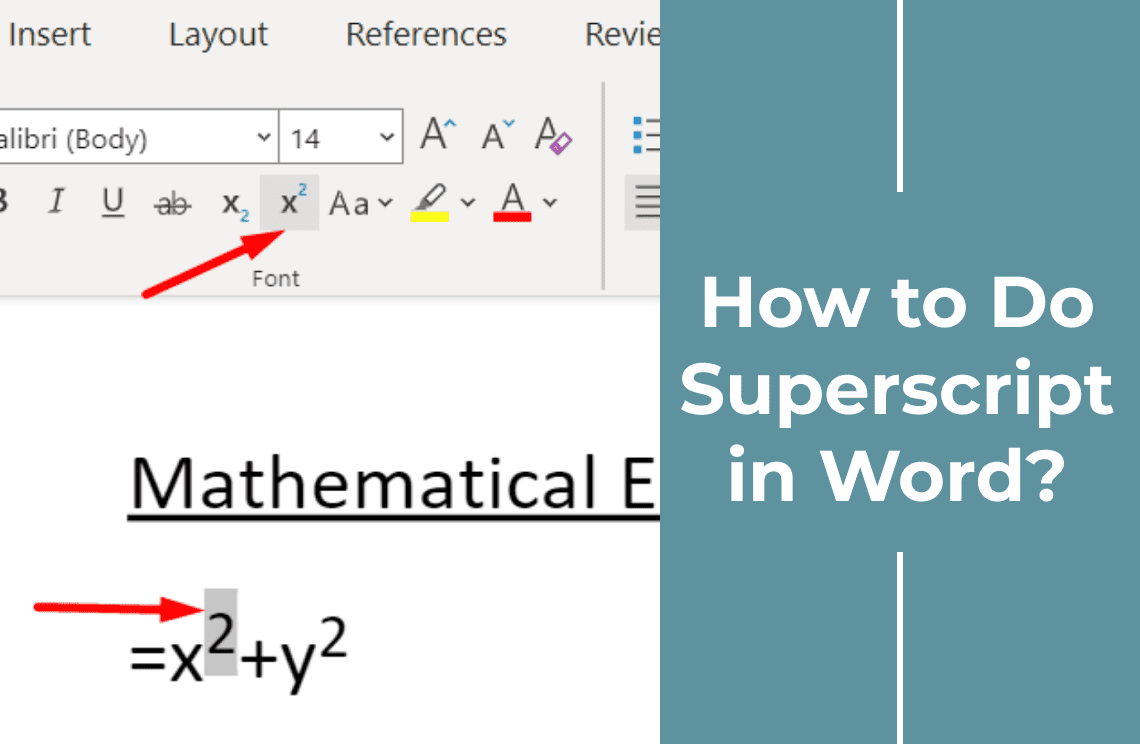
Method 1: Using the Superscript Button in Word

Using the superscript button in Word is a straightforward method to format text:
- Highlight the text you want to convert to superscript.
- Navigate to the "Home" tab on the Ribbon.
- Locate the "Superscript" button, which looks like an "X²," in the Font group.
- Click on the "Superscript" button to apply the formatting.
Once clicked, your selected text will be converted to superscript. To revert, highlight the superscript text and click the button again. This method ensures quick and easy application of superscript formatting in your document.
Method 2: Keyboard Shortcut for Superscript
Using keyboard shortcuts is an efficient way to format text as superscript:
For Windows: Press Ctrl + Shift + +
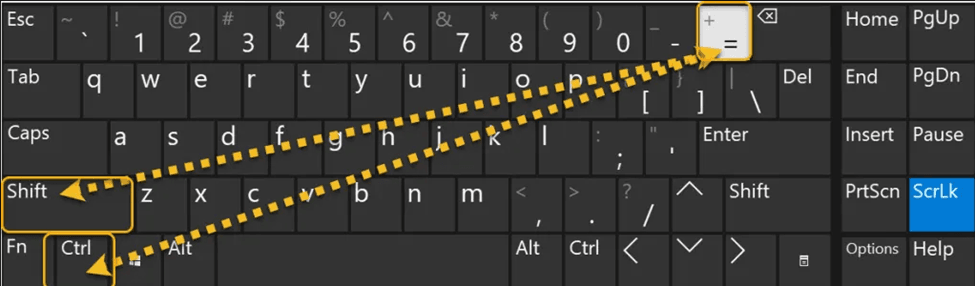
For Mac: Press Command + Shift + +
For example, to write the chemical formula H₂O in Word, you would type "H2O," and then highlight the "2." Press the respective keyboard shortcut for your operating system to switch the "2" to superscript, resulting in H₂O. Keyboard shortcuts streamline the process, allowing you to quickly apply superscript formatting without navigating through menus, enhancing your productivity.
Method 3: Using the Font Dialog Box
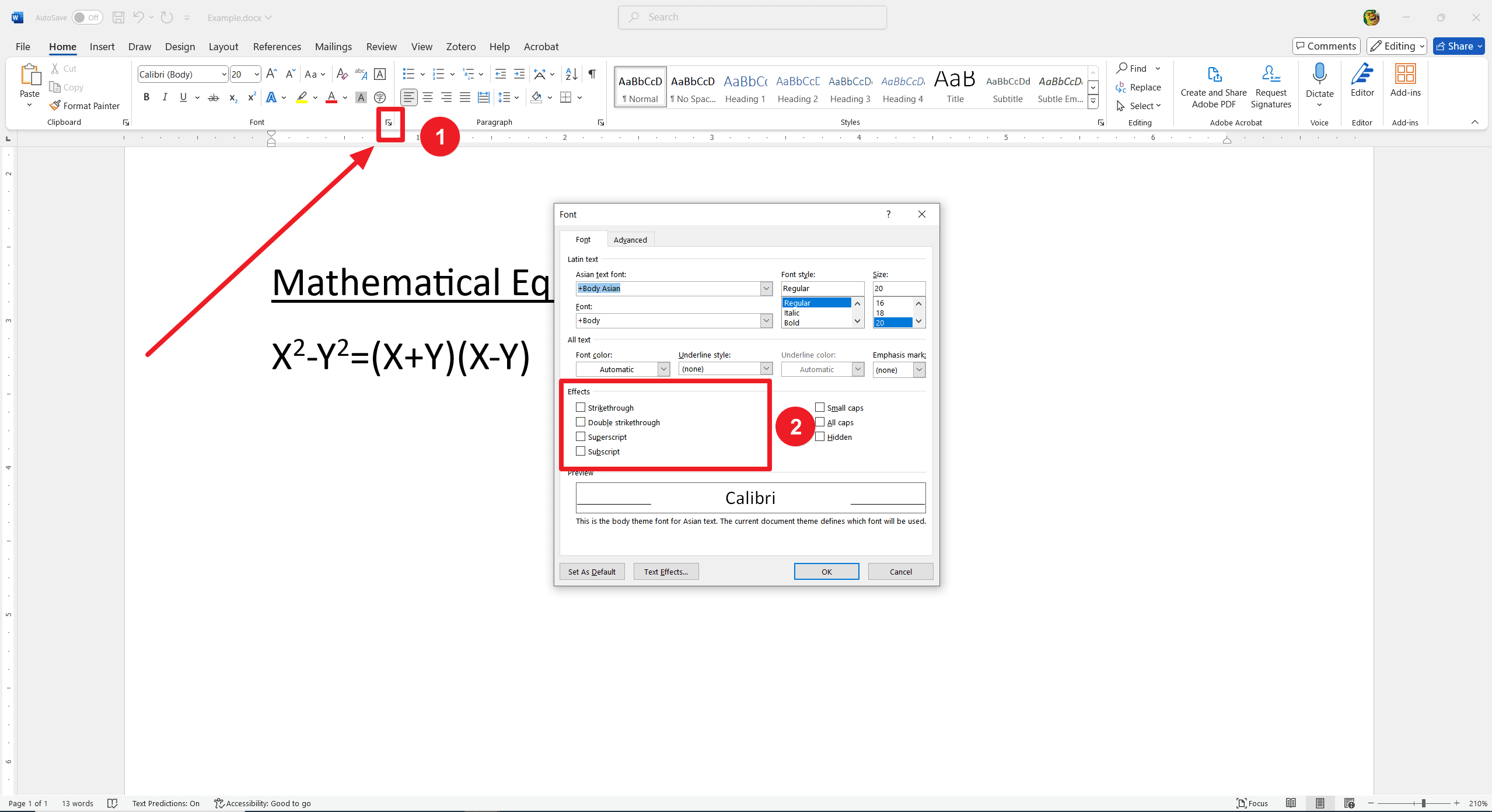
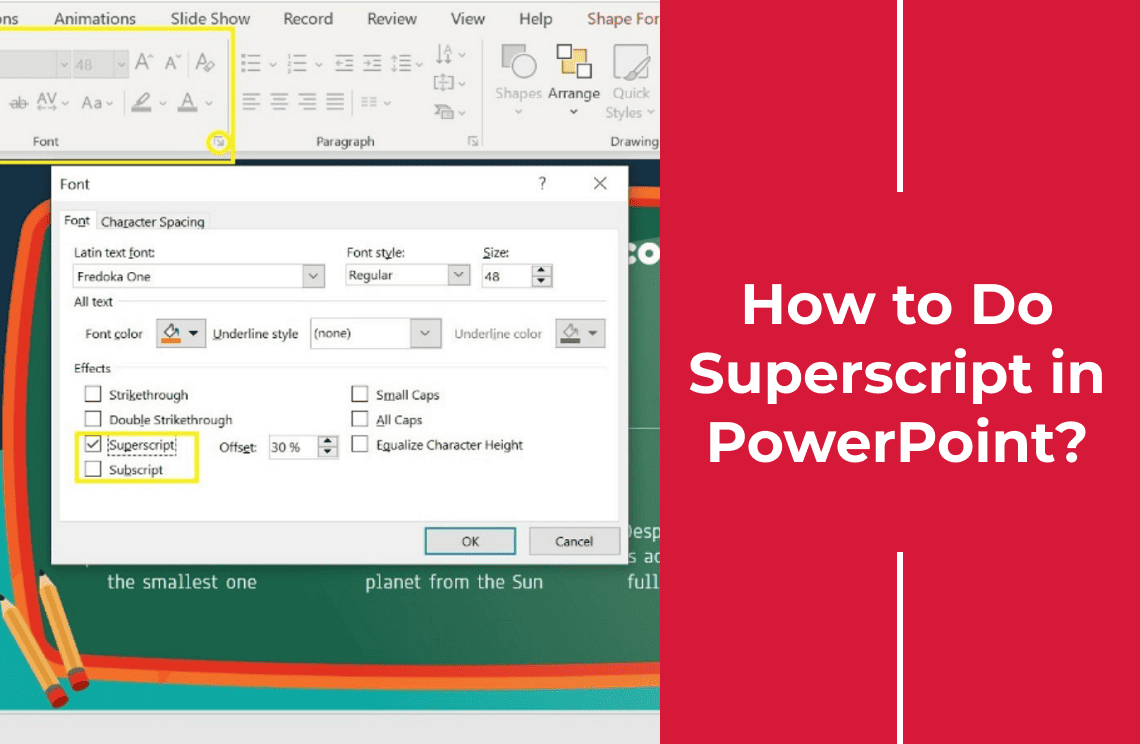
To use the Font dialog box for superscript formatting, follow these steps:
- Highlight the text you want to format as superscript.
- Right-click the highlighted text and select "Font" from the context menu.
- In the Font dialog box that appears, look for the "Superscript" option under the Effects section.
- Check the "Superscript" box.
- Click "OK" to apply the changes.
Your selected text will now appear as superscript. This method allows for greater precision and additional formatting options within the dialog box.
Method 4: Adding Superscript through Equation Editor
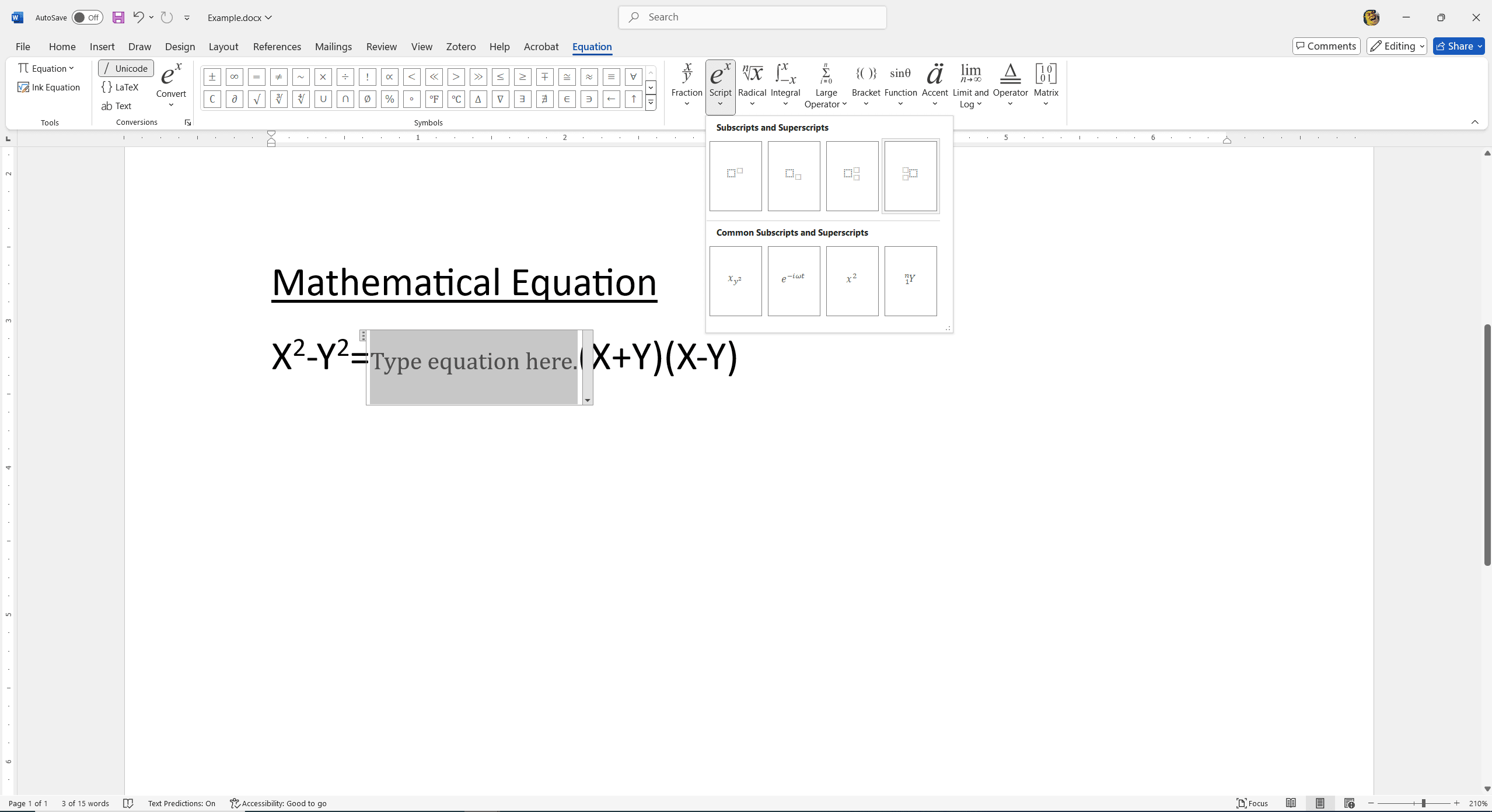
The Equation Editor in Word is a powerful tool for adding superscripts, especially in complex mathematical or scientific documents:
- Navigate to the "Insert" tab on the Ribbon.
- Click on "Equation" in the Symbols group. It will open a new equation box and the Equation Tools Design tab.
- In the Equation Tools Design tab, look for the "Script" button and click on it.
- Select the superscript format (a placeholder with a box arranged above another box).
Now, type your base text in the lower box and your superscript text in the upper box. This method is particularly useful for creating neatly formatted equations and scientific notations.
Examples and Use Cases
Superscript formatting is widely used across different fields. Here are some common examples:
- Mathematical Expressions: Superscript is essential for denoting powers and exponents, such as (x^2) or (e^{i\pi} + 1 = 0).
- Chemical Formulas indicate the number of atoms in chemical compounds, such as H₂O for water and CO₂ for carbon dioxide.
- Footnotes and Citations: Superscripts are commonly used in academic writing to reference footnotes or endnotes, like this example¹.
These use cases illustrate the importance of superscript in various disciplines, ensuring clarity and precision in documentation.
Conclusion
Incorporating superscripts in Word is a straightforward process with multiple methods to suit your preference, whether using keyboard shortcuts, the Font dialog box, or the Equation Editor. These tools enhance the utility and presentation of your documents, particularly in fields like mathematics, chemistry, and academic writing. Mastering superscript formatting streamlines document creation, providing clarity and professionalism. By efficiently applying these techniques, you can elevate your work's readability and precision.